How AI Detectors Actually Work: The Truth About Undetectable AI Tools
 Oleksandra Zhura
Oleksandra Zhura
AI tools and detectors are locked in a fierce battle as the global AI market races toward $826 billion by 2030. AI writing tools continue to grow rapidly at a 25% compound annual growth rate. This growth has led to AI-generated content becoming accessible to more people in any discipline.
Detection technology’s reliability raises serious concerns. Current detectors get it right only 7 out of 10 times. Tests reveal a more worrying trend – 10% to 28% of human-written content gets wrongly marked as AI-generated. These errors happen because detectors look at text metrics like perplexity and burstiness. AI content shows more predictable patterns compared to human writing.
This piece dives deep into detection mechanisms and reveals the best tools available now. We’ll look at platforms that claim 99 %+ accuracy rates. Content creators, educators, and business professionals need to understand how detection tools work and how to responsibly manage the presence of AI-generated content. Understanding these detection tools has become crucial in today’s digital world.
What Are AI Detectors and Why Do They Matter

AI detectors are specialized software tools that analyze text to determine if a human or AI system wrote it. These tools look at writing patterns, sentence structure, and language characteristics to tell human and machine-created content apart. Unlike regular plagiarism checkers that look for matching content, AI detectors focus on spotting the unique signs of AI writing.
AI detectors vs AI generators: the growing need
The rapid rise of AI text generators has created an urgent need for reliable detection methods. AI generators have become so advanced that telling machine-written text from human writing is getting harder. Studies show that teachers and editors find it extremely hard to spot whether ChatGPT or a human wrote a piece of content.
This problem exists because AI-generated text rarely has obvious mistakes that would give away its artificial source. Detection remains vital since bad actors use AI writing tools to spread false information online and create profit-driven content.
Generators and detectors are locked in a classic tech arms race. One professor put it simply: “It’s a proverbial game of cat and mouse”. Detection tech improves, and generator models adapt to create more human-like text. This ongoing battle makes it essential to understand how both technologies work.
Yet no AI detection service has conclusively identified AI-generated content at a rate better than random chance as of mid-2024. This creates major problems for people who need these tools to verify content.
Who uses AI detectors today?
Several key groups depend on AI detection technology, though their confidence levels vary:
- Academic institutions use AI detectors to spot possible academic misconduct in student work. Schools and universities run these tools to stop cheating and protect academic integrity. One detection tool markets itself by saying it offers “a reliable solution for professors, teachers, and universities to verify their students’ work”.
- Content managers and publishers use these tools to check if submitted materials are original, especially now that AI-generated content floods publishing channels.
- SEO professionals need these tools to maintain quality human-written content that ranks well in search results.
- Business organizations use detection technology to stop AI-generated misinformation that could hurt their brand’s reputation.
Anyone who cares about content authenticity might find these tools helpful, though their effectiveness remains debatable.
Common misconceptions about AI detection
Several myths about AI detection technology need clearing up:
- Misconception #1: AI detectors are 100% reliable
No AI detection software gets it right every time. These tools work with probabilities rather than certainties, which makes them fundamentally different from plagiarism checkers. A January 2025 study showed AI detectors remain “consistently inconsistent.” They sometimes approach accuracy but give different scores on similar content in later checks.
- Misconception #2: Detection tools provide conclusive evidence
Many people wrongly think a high AI probability score proves everything. Research shows these tools often flag human writing as AI-generated and produce uncertain results. Schools can’t rely on them alone for academic integrity cases.
- Misconception #3: All AI detectors function similarly
Each detection tool uses its own algorithms and training data, which leads to very different results. A detailed study showed that “AI detection tools were more accurate in identifying content generated by GPT 3.5 than GPT 4“. This proves their performance changes based on the AI model they’re trying to detect.
- Misconception #4: AI detection can’t be circumvented
Although some tools attempt to make AI-generated text sound more natural, relying on such methods raises ethical and academic integrity concerns. However, one study concluded that “we should assume students will break any AI-detection tools, whatever their sophistication”.
- Misconception #5: AI detectors are just for catching cheaters
These tools do more than catch academic dishonesty. Turnitin explains that their “AI writing detection feature is simply a tool that gives educators a report with data points”. This helps start conversations about proper AI use instead of just punishing students.
These misconceptions matter to anyone who relies on AI detection technology, especially as the line between human and AI-generated content gets blurrier. Detection methods will keep evolving, and so will ways to create undetectable AI content. This tech battle remains one of the most important in digital content creation.
How AI Detectors Actually Work
Modern AI detectors pack sophisticated technology that can tell human writing from machine-generated text. These tools go beyond simple pattern matching and run complex algorithms that look at many aspects of writing at once.
1. Classifiers and training data
Machine learning classifiers form the heart of AI detectors. These algorithms learn to sort text as either human-written or AI-generated by studying huge datasets with examples of both types.
The detection systems typically work like this:
- Training phase: The classifier studies labeled examples of human and AI-generated writing.
- Analysis phase: The detector looks for linguistic patterns and structural features in new text.
- Classification decision: The system gives a probability score based on its training that shows if the content came from AI.
These classifiers use various machine learning algorithms such as Decision Trees, Logistic Regression, Random Forest, and Support Vector Machines. Each algorithm spots different text patterns.
OpenAI’s classifier learned from paired samples of human-written and AI-generated text about similar topics. Their system can spot about 26% of AI-written text as “likely AI-generated.” However, it wrongly labels about 9% of human-written text as AI-generated.
2. Embeddings and semantic analysis
AI detectors use embeddings to turn words into numbers that capture meaning relationships. These embeddings place words as mathematical coordinates in a complex space where related meanings cluster together.
These embedding models help detectors:
- Turn words into vector coordinates based on meaning and usage
- Build a “semantic web” with related words closer together
- Study how these vectors match patterns in AI-generated content
The detection systems run several types of analysis on these embeddings:
- Word frequency analysis: Spots repetitive patterns common in AI writing
- N-gram analysis: Studies how phrases fit within specific contexts
- Syntactic analysis: Looks at grammar patterns that might reveal AI writing
- Semantic analysis: Checks meaning, including metaphors and cultural references
The detector creates embedding vectors for new text and compares them to known AI patterns. Text that matches AI patterns closely gets higher scores for being machine-generated.
3. Perplexity and burstiness explained
Perplexity and burstiness serve as key metrics that help spot differences between human and AI writing styles.
Perplexity shows how predictable each word appears in context:
- Predictable text shows lower perplexity and flows smoothly
- Creative language choices and typos lead to higher perplexity
- AI tends to generate text with lower perplexity by picking the most likely next word
AI detectors look for suspiciously predictable text that might signal AI generation.
Burstiness looks at how sentences vary in structure and length:
- Little variation means low burstiness
- Human writing shows higher burstiness with more varied sentences
- AI usually creates content with lower burstiness and similar sentence patterns
These metrics have limitations. A study found that perplexity-based detectors sometimes label prominent historical documents like the Declaration of Independence as AI-generated. This happens because these documents appear often in AI training data, making them seem predictable.
The specific language model used affects perplexity measures, which creates differences between detection tools. This explains why current AI detectors sometimes disagree when analyzing the same text.
The Tools Behind the Detection: Top AI Detectors in 2025
The AI content detection market is growing fast. Experts predict a 24% yearly growth through 2030. Several sophisticated tools now lead the way in spotting AI-written content. Each brings its own method to identify artificial content in this complex field.
Litero AI and its detection models
Litero AI goes beyond simple AI detection. This platform works as a detailed academic writing assistant. It stands out by mixing detection tools with features that help improve writing. We are focused on maintaining academic honesty. The system checks text immediately and looks for copied content at the same time.
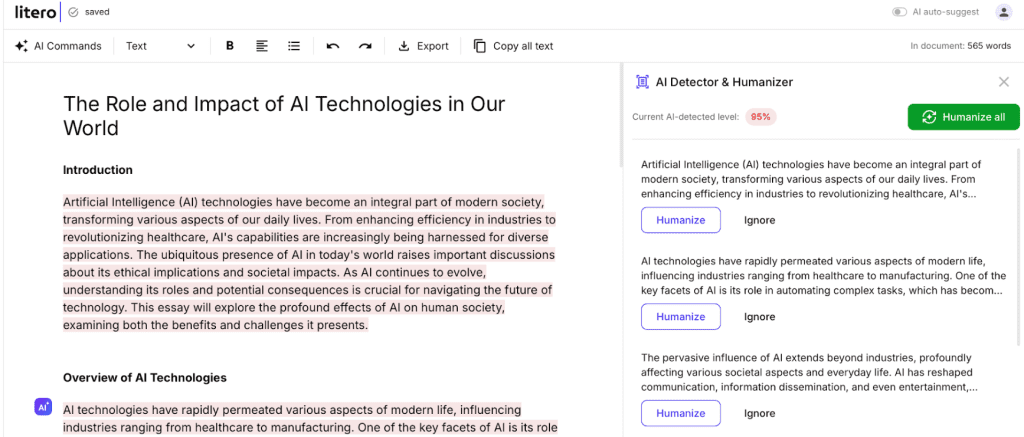
Litero’s unique strength lies in its supportive approach that empowers students through every stage of the writing process. The platform has a style enhancement tool that helps users adjust flagged text while keeping their own voice. Students find this two-way feature helpful. They can spot problems and fix them right away. So, it is one of the best AI detectors for students because it combines detection with writing improvement tools.
Winston AI, GPTZero, and others compared
Winston AI, a 2022 Canadian startup, boasts a 99.98% accuracy rate in catching AI-generated content. The system uses color-coded maps to show how predictable text is – a key sign of AI writing. Winston AI catches content from major LLMs like ChatGPT 4.0, Google Gemini, and Claude. The company says it can spot paraphrased content from tools like Quillbot, too.
GPTZero, launched in 2022 in the United States, uses perplexity and burstiness metrics to detect AI content. Their website claims 99% accuracy for human text and 85% for AI content. Tests by others suggest it might not be as accurate as Winston AI.
Other strong players include:
- Originality.AI: Content marketers and SEO experts love this tool. It spots GPT-4 content with 98-99% accuracy
- Copyleaks: Popular with marketers and plagiarism checkers who work in many languages
- Turnitin: A trusted name in schools that now faces questions about its AI detection accuracy
Recent tests show mixed results across these tools. Only three detectors caught every AI-written piece in one big test. Many tools also wrongly label human writing as AI-generated. This shows how tricky accurate detection can be.
Free vs paid AI detector tools
Price matters when picking an AI detector. GPTZero offers free basic checks and paid plans from $15/month (150,000 words) to $35/month (500,000 words). Winston AI starts at $19/month and includes both AI detection and plagiarism checking.
Free tools come with clear limits. Leap AI allows two free checks per day (20,000 characters each). Smodin gives five free scans (5,000 characters each). Basic versions skip advanced features like detailed reports, plagiarism checking, and multiple language support.
Big organizations need reliable tools that can handle lots of text. They usually choose paid options. Schools, content companies, and publishers see this as a good investment. The stakes in AI content detection keep rising. Most premium tools now offer different plans to fit various needs as the market grows.
The Rise of Undetectable AI Tools
The rise of AI detection technologies has sparked a new industry of “undetectable AI” tools, leading to an ongoing technological arms race. People can only tell AI-written text from human-written text 53% of the time, just a bit better than guessing. This challenge has created a whole new type of software that helps AI content slip past detection.
What is an AI humanizer?
AI humanizers are tools that make machine-written text sound more natural and human-like. These tools change AI content by tweaking word choices, sentence structures, and overall tone. This makes the content more relatable and engaging. They bridge the gap between robotic AI output and genuine human writing.
AI humanizers offer several key features:
- They adjust their tone to match what readers expect
- They restructure sentences for better flow and readability
- They pick better words to replace mechanical phrases
- They break up patterns that give away AI writing
A trusted industry source points out a big problem: “70% of AI-generated content doesn’t pass detection tools and reads like a robot wrote it”. Tools that improve tone and clarity may be useful, but students and professionals should avoid altering content for the sole purpose of evading detection.
How bypass tools work
These tools use smart algorithms to change text features that AI detectors usually catch. They look for patterns that might trigger detection tools and rewrite those parts while keeping the original message.
Different platforms use different methods, all of which focus on the same:
- Perplexity manipulation – They add creative language to make the text less predictable
- Burstiness enhancement – They mix up sentence lengths and structures
- Statistical pattern disruption – They remove repeated phrases that AI detectors look for
Many services now use special “rewriter engines” that don’t just change content—they raise its quality through complex processes.
Limitations of current detection models
Detection tools don’t deal very well with several challenges that bypass tools exploit. Here are the biggest problems:
False positives on human writing – Detection tools often mistake real human writing for AI content. Tests showed multiple detectors labeled a hand-written summary as “likely AI-generated”.
Inconsistent performance across AI models – Tools work differently with various AI models. They catch GPT-3.5 content more easily than GPT-4 output. This creates a constant game of catch-up with newer models.
Bias against non-native English writers – The tools unfairly flag content from non-native English speakers as AI-generated. This raises ethical concerns about using these tools to evaluate academic or professional work.
Limited transparency in methodology – Most detection tools work like “black boxes”—they get results but don’t explain their decisions. Nobody knows why some texts pass while others fail.
The success of undetectable AI tools reveals a basic truth: without tracking content back to its AI source with exact settings, these determinations can be fooled. Security experts call this a “cat and mouse game” between AI creators and detectors. Detection technology always lags behind smarter content generators. This highlights the need for transparency and ethical policies around AI-generated content to ensure responsible usage.
Can You Really Bypass AI Detectors?

Studies show AI detection tools aren’t foolproof or reliable. Tests reveal 96% accuracy in spotting human-written text. This drops by 20% for machine-translated human content. About 20% of AI-generated texts slip through undetected.
Common bypass strategies and their success rates
People use several methods to get around AI detection tools successfully:
- Simple modifications to text, like removing commas or rewording, can significantly lower detection rates
- Text paraphrasing tools make AI text look human-written, and detection accuracy falls to 26%
- Some unethical tactics attempt to exploit detector weaknesses, such as character substitution, but these practices violate academic and professional norms
- Adding emotion or the word “cheeky” in prompts tricks detectors 80-90% of the time by adding irreverent metaphors
Tools like Litero AI proved highly effective, as they focus on refining content quality and structure. However, users must still ensure the final work reflects their original thinking and meets ethical standards. Regular ChatGPT content had a 10% detection rate.
How to humanize content
You can make AI-generated text more human through several proven techniques. Word choice and tone adjustments create clearer, more compelling content. Personal stories, examples, and firsthand experiences add a unique touch that AI can’t easily copy.
Combining sentences into complex structures and adding emotional elements works well, too. Stories and ground examples make the content engaging and harder to spot as AI-generated.
Why some detectors fail on models like Claude
Claude AI poses unique challenges to detection tools because it copies human writing styles with exceptional accuracy. Claude stands out by using sophisticated language patterns and adding strategic variety to its content.
Test results show Claude creates fresher, more original content than ChatGPT with fewer AI patterns. Winston AI emerged as the only tool that could spot Claude 2’s outputs consistently, which proves Claude’s skill at generating human-like text.
Detection tools face a fundamental challenge. Without tracking content right from its creation point, these tools remain vulnerable to manipulation.
The Future of AI Detection: What Comes Next?
The battle between AI content creators and detectors has entered a new phase. Both sides continue to develop sophisticated tools. AI detection still remains inconsistent, but new technologies could revolutionize this digital world.
Watermarking and new detection methods
Watermarking stands out as the most promising breakthrough in reliable AI content identification. Google’s SynthID now guides this innovation by embedding imperceptible digital watermarks directly into AI-generated images, audio, text, and video without affecting content quality. These watermarks stay detectable even after changes like cropping, adding filters, or compression.
SynthID can watermark just three sentences of text. The accuracy gets better with longer text samples. Google published this technology in Nature and made it available through their Responsible Generative AI Toolkit in October 2024.
The biggest problem with these watermarking techniques comes from implementation challenges. Model developers need to cooperate first. Recent analysis shows that “Watermarking is not a ‘universal’ detection solution… The watermark implemented by one model developer only lets them later verify whether content was generated by their own model”.
The arms race between AI writers and detectors
Security researchers describe this technological contest as “an ongoing technological arms race”. New AI models keep emerging, and detectors must update constantly. One expert calls this “an arms race that nobody asked for”.
Undetectable AI tools now manipulate perplexity and burstiness to avoid detection. Newer AI models vary their writing styles intentionally to stay hidden. This endless cycle of adaptation makes consistent detection harder each day.
What users should expect in the next 2 years
The near future points to several key developments:
- AI detection middleware will grow more sophisticated, making generative AI more trustworthy and available
- Multimodal AI will process data from various sources to enable nuanced detection methods
- Stronger governance frameworks will emerge as companies balance breakthroughs with regulatory compliance
The most effective developments will focus on governance, middleware, and training techniques that build trust in AI. Academic institutions might move away from unreliable detection software. They could adopt better policies and teaching methods that use AI responsibly instead.
Conclusion
AI detectors and undetectable AI tools continue their unbalanced battle in 2025. Current detection technology fails to achieve perfect accuracy. Error rates range from 10-28% for human content, and about 20% of AI-generated text remains completely undetected. Technology advances faster through breakthroughs like Google’s SynthID watermarking.
People who rely on AI detection should set realistic expectations. Detection tools serve as helpful guides rather than definitive arbiters. Academic institutions, content managers, and publishers should know that detection is just one part of a complete approach to content verification. These tools’ biggest problems include false positives, bias against non-native English writers, and inconsistent performance with different AI models.
This technological arms race will continue without doubt as both sides develop more sophisticated methods. Detection tools will become more nuanced. Undetectable AI will keep finding creative ways to bypass detection. The focus has ended up changing from “Can AI content be detected?” to “How should we combine AI smoothly into our content creation processes?”
The most practical solution might not be perfect detection. Instead, thoughtful governance frameworks could acknowledge AI’s role in content creation while maintaining standards for transparency and authenticity. Understanding these technologies’ workings enables users to make informed decisions about when and how to use both AI generation and detection tools. This balance will shape content creation over the last several years.
FAQs
Q1. How do AI detectors actually work?
AI detectors analyze text using machine learning algorithms that examine patterns in writing style, sentence structure, and word choice. They compare these patterns to known characteristics of AI-generated text, looking at factors like perplexity (predictability of word choices) and burstiness (variation in sentence length and complexity).
Q2. Are AI detectors always accurate?
No, AI detectors are not 100% reliable. They can produce false positives (incorrectly flagging human writing as AI-generated) and false negatives (failing to detect AI-written content). Accuracy rates vary, but even leading detectors can have error rates of 10-30%.
Q3. Can AI-generated content truly be undetectable?
While it’s becoming increasingly difficult, some specialized tools and techniques can help AI-generated content evade detection. These include AI humanizers, which modify text to appear more natural, and methods that manipulate linguistic patterns that detectors look for. However, as detection technology improves, maintaining undetectability becomes an ongoing challenge.
Q4. What are some limitations of current AI detection technology?
Current AI detectors face several challenges, including inconsistent performance across different AI models, potential bias against non-native English writers, and difficulty distinguishing highly polished human writing from AI-generated text. Additionally, they often lack transparency in their methodology, making it hard to understand why certain texts are flagged.
Q5. What does the future hold for AI detection?
The future of AI detection is likely to involve more sophisticated techniques like digital watermarking, which embeds imperceptible markers directly into AI-generated content. We can also expect to see improvements in multimodal AI that can analyze diverse data inputs for more nuanced detection. However, the ongoing technological arms race between AI generators and detectors means this field will continue to evolve rapidly.
Cite this article
We encourage the use of reliable sources in all types of writing. You can copy and paste the citation manually or press the “Copy reference” button.
Zhura, O. (2025, May 11). How AI Detectors Actually Work: The Truth About Undetectable AI Tools. Litero Blog. https://litero.ai/blog/how-ai-detectors-actually-work-the-truth-about-undetectable-ai-tools-2025-guide/
Was this article helpful?

Oleksandra Zhura
Content Writing SpecialistOleksandra is a content writing specialist with extensive experience in crafting SEO-optimized and research-based articles. She focuses on creating engaging, well-structured content that bridges academic accuracy with accessible language. At Litero, Oleksandra works on developing clear, reader-friendly materials that showcase how AI tools can enhance writing, learning, and productivity.
-
Academic writing copilot built for students
-
10M+ sources from academic libraries
-
Built-in detectors with transparency tools
-
Context-aware suggestions as you write
